Home Charging
Choosing An Electric Vehicle Charging Station
For every plug-in vehicle and parking spot there is a charging station solution. Almost any Level 2 EVSE (electric vehicle supply equipment) can handle overnight charging for most vehicles, and most homes have enough electrical capacity to accommodate Level 2 charging. Most customers will need far less charging power than they might think before living with an EV. Drivers in the US average 37 miles per day!
We’re happy to help you select and install the ideal charging solution for you and your plug-in vehicle’s charging needs. Here’s a video explaining how to select the right EV charging station for your driving needs.












How Many Miles Of Charge Per Hour
We can estimate the number of “miles of charge per hour” any charger can provide once we know two factors, the efficiency of the electric vehicle and the EV charging station’s amperage (speed).
An efficient EV will average 4.0mi/kWh (miles per kilowatt hour). An average level 2, 240V (Volts) hardwired home charger might be rated at 32A (Amps) or 7.68kW. (240 Volts X 32 Amps = 7,680 Watts or 7.68kW.) Charging at 7.68kW with a vehicle that drives 4.0mi/kWh provides 30.72 miles of range per hour. A charger with higher amperage decreases charge time and increases the amount of miles of charge per hour. An EV charger with lower amperage increases charge times and decreases the amount of miles of charge per hour.
Most drivers rarely charge their EV’s from 0-100%. If an EV with 250 miles of range plugs in with 20% left on the battery (50 miles), it needs 200 miles to fully recharge. Using an average level 2, 240V charger providing 30.72 miles of range per hour, it would take 6.51 hours to fully charge.
But this is all stuff you’ll likely never think about. Just get home, plug in and start the next day with a fully charged vehicle!
240V Outlets And Plug-in EV Charging Stations
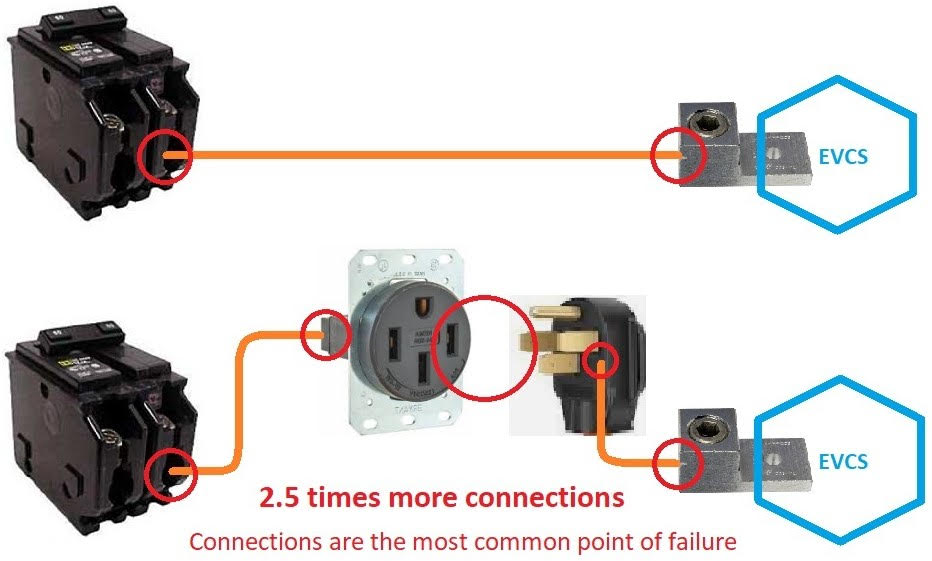
We have a company policy of only installing hardwired EV charging stations for several reasons. Newer electrical codes require using GFCI breakers when connected to outlets in high moisture locations like a garage or on the exterior. GFCI protected breakers cause nuisance tripping when used with EV charging. Until there are changes to Washington’s electrical code, pairing 240V outlets with plug-in EV charging stations will be problematic.
Another consideration is that these outlets were designed decades ago and weren’t intended for the long, sustained loads that EV chargers place on them. The industry is seeing high failure rates of 240V outlets when used with plugged-in EV chargers.
Some EV charging station safety advice from industry experts.
Outlets have five connection points versus just two on a hardwired install, increasing the number of potential failure points. Given that, we made the decision we won’t install or warranty something with such a high potential failure rate.
Here’s an article about 240V outlet issues in Washington State. We’re here as green energy and transportation enthusiasts. We want to ensure our customers have a reliable and safe home charging experience.
We suggest keeping a portable level 1 or level 2 plug-in charger in your trunk. It’s quite handy in the summer on road trips and camping situations without GFCI breakers.
EV Charging Station Financial Incentives
There is a Federal tax incentive of 30% and no sales tax, (roughly 10%) toward the costs of EV charging stations, labor, materials and permits.
In Seattle, there is a time-limited rebate being offered by Seattle City Light and Platt …